Engineering considerations in leakage assessments
How we approach leakage assessments across seals, flanges, and composites using real-world methods and advanced FEA.
In this blog post, we explore the key considerations and methods behind leakage assessments across a range of seal types and pressure conditions. This work is grounded in detailed project studies and simulation techniques used in real-world engineering assessments.
We cover sealing systems including Mechanical Seals, O-Rings, Pressure-Activated Seals, Flanges, Face Gaskets, and Ring Type Joints (RTJs). These components are critical in maintaining integrity under both standard and extreme operating conditions.
Normal flange checks
For standard flange connections i.e. non high-pressure (HP) and non high-temperature (HT) scenarios – typical assessments follow simplified engineering methods such as those found in Kellogg guidelines.
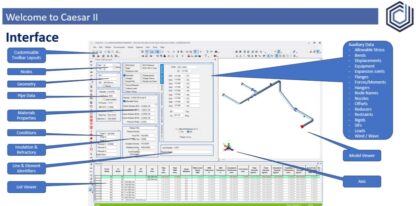
These checks often use Pipe Stress Analysis methods, or Design by Rule Pressure Vessel methods from the likes of: Caesar II, ROHR2, AutoPipe, PVElite, or other tools for a global system assessment.
High temperature high pressure seals
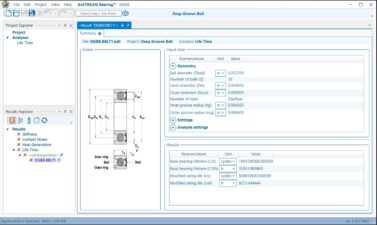
When dealing with high pressure and high pressure conditions, typical issues to consider include: creepage, preload maintenance, relaxation and leakage, cyclic loadings resulting in ratcheting and ductility exceedance/failure.
ABAQUS FEA modelling
To address these issues, Finite Element Analysis (FEA) via Abaqus is the chosen method. This includes:
- Large deformation
- True Stress/Strain material properties as a function of temperature
- Spiral wound gasket approximation per ASME VIII Div 2
- Contact Pressure conformation to code
- Pressure penetration check – an indication of leakage and a change of boundary conditions (i.e. increased separation pressure loads)
- Pre-load sequencing and subsequent relaxation check
- Primary and Secondary stress checks and Creep life checks
- Ratcheting assessment and loss of preload
- Fatigue assessment to ensure integrity of connection and seal are maintained over many cycles,
- Serviceability check – to ensure flanges assembly stay intact
GRP/Plastic/General Composite
For GRP and composite-based systems, typical issues to consider include: crushing, fibre failure, matrix failure, large expansion rates, pressure intensified displacements.
Ansys FEA Modelling
Composite system assessments require detailed Ansys-based simulations incorporating:
- Layup information (plies, thickness, draping, matrix,
directional parameters) - Failure criteria – fibre/matrix/face/code of practices
- Fatigue
- Overload and crushing
- Chemistry and temperature effects on matrix
- Large deformation
- Serviceability check – to ensure flanges assembly stay intact
Need support with sealing challenges or leakage assessments?
DOCAN specialises in exactly this – from code-based evaluations to advanced FEA for high pressure and high temperature systems. Whether you’re troubleshooting existing issues or designing for long-term integrity, we’re here to help. Get in touch with us to discuss your project.